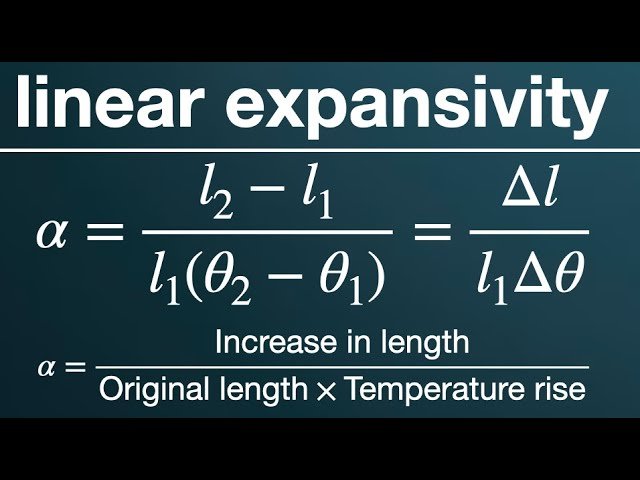
Linear expansivity quantifies the change in length of a material per unit temperature variation. This property plays a crucial role in various fields, from engineering to physics. Understanding how materials expand linearly is essential for designing structures that can withstand temperature fluctuations. By studying the effects of linear expansivity, engineers can create more durable and reliable products. Join us as we delve deeper into the fascinating world of linear expansivity and explore its practical applications and implications.
Exploring Linear Expansivity: Understanding How Things Expand and Contract
Welcome, curious minds! Today, we are going to dive into the fascinating world of linear expansivity. Have you ever wondered why bridges have expansion joints or why a metal rod feels different in summer compared to winter? Well, all these phenomena are connected to the concept of linear expansivity. So, let’s embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of how objects expand and contract with changes in temperature.
The Basics of Linear Expansivity
Linear expansivity, also known as thermal expansion, is a property of matter that describes how its dimensions change in response to temperature variations. In simpler terms, when things heat up, they typically expand, and when they cool down, they contract. This phenomenon is a fundamental aspect of nature and has practical implications in various fields, from construction to everyday household items.
Think about a rubber band – have you noticed how it gets tighter when you hold it close to a heat source or how it loosens up when left in a cold place? That’s linear expansivity at work! Now, let’s delve deeper into the concepts and mechanisms behind this intriguing property.
Understanding Linear Expansion
Linear expansion refers to the change in length of an object due to temperature changes. Different materials have varying degrees of linear expansivity, which is typically measured in terms of a coefficient that indicates how much a material expands per degree Celsius. For example, metals generally have a higher coefficient of linear expansion compared to non-metallic substances like wood or plastic.
When an object is heated, its particles gain energy and start vibrating more vigorously, causing the material to expand. Conversely, cooling reduces the particle movement, leading to contraction. This back-and-forth dance of expansion and contraction is a vital aspect of how materials respond to thermal energy.
Practical Applications of Linear Expansivity
Linear expansivity plays a crucial role in various real-world scenarios. One common application is in the design of structures such as bridges, roads, and railways. Engineers have to account for the expansion and contraction of materials when constructing these infrastructures to prevent damage from temperature-induced stresses.
For instance, when a metal bridge is exposed to the sun, it tends to expand due to the heat absorption. Without proper expansion joints that allow for this elongation, the bridge could buckle or warp, compromising its structural integrity. By understanding and applying the principles of linear expansivity, engineers ensure the safety and longevity of such vital constructions.
Everyday Examples of Linear Expansivity
Linear expansivity isn’t just limited to grand structures; it affects everyday objects too. Have you ever noticed how a glass jar may be difficult to open when hot but loosens up after running it under cold water? This is because the metal lid and glass jar have different coefficients of linear expansion, causing them to expand and contract at different rates.
Similarly, in cooking, understanding how materials expand and contract can be crucial. Baking trays, for instance, may warp if subjected to rapid temperature changes, impacting the quality of your baked goods. By being aware of linear expansivity, you can adjust your cooking methods to ensure consistent results.
Factors Affecting Linear Expansivity
Several factors influence the linear expansivity of materials. One primary factor is the atomic structure of a substance. Solids with closely packed atoms tend to have lower expansivity compared to those with looser atomic arrangements. This is why metals, with their tightly packed crystal structures, often exhibit significant expansion under heat.
Additionally, the type of bonding between atoms in a material affects its expansivity. Substances with strong bonds, such as metals, generally have higher coefficients of linear expansion than those with weaker bonds like plastics. Understanding these structural differences is key to predicting how materials will behave under changing temperatures.
Measuring Linear Expansivity
Scientists and engineers use various methods to measure the linear expansivity of materials accurately. One common technique involves subjecting a sample to controlled temperature changes and monitoring its dimensional variations using precise instruments. By calculating the change in length relative to the initial size and temperature change, researchers can determine the coefficient of linear expansion for a given material.
These measurements are essential for designing efficient systems and predicting the performance of materials in different environments. Understanding how a substance responds to temperature fluctuations enables us to develop safer, more durable products and structures.
Practical Implications of Linear Expansivity
Now that we have explored the fundamentals of linear expansivity, let’s consider some practical implications of this concept in our daily lives. From the buildings we inhabit to the devices we use, linear expansivity influences numerous aspects of our modern world.
Construction and Engineering
In the field of construction and engineering, linear expansivity is a critical consideration. Building materials such as concrete, steel, and glass have distinct coefficients of expansion, necessitating careful planning to accommodate thermal fluctuations. Failure to address these thermal stresses can result in structural deformations and potential safety hazards.
By incorporating expansion joints, flexible materials, and other design features that account for linear expansivity, architects and engineers can create resilient structures that withstand temperature variations and environmental factors. From skyscrapers to residential homes, the principles of linear expansivity shape the built environment around us.
Manufacturing and Product Design
In the realm of manufacturing and product design, understanding and harnessing linear expansivity are essential for producing high-quality goods. From electronics to automobiles, modern products are made up of various materials that expand and contract differently under thermal stress.
By conducting thorough testing and analysis of materials’ expansivity characteristics, manufacturers can develop products that perform reliably across a range of temperatures. This attention to detail ensures that devices function optimally in diverse climates and conditions, enhancing user experience and product longevity.
Thermal Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Linear expansivity also plays a role in thermal insulation and energy efficiency. Materials with high coefficients of expansion, such as metals, can contribute to heat loss in buildings if not properly insulated. Understanding how different materials expand and contract enables architects and builders to select appropriate insulation materials that minimize thermal conductivity and maintain indoor comfort.
By optimizing the thermal performance of structures through intelligent material selection and design practices, we can reduce energy consumption, lower utility costs, and promote environmental sustainability. Linear expansivity thus emerges as a key factor in achieving energy-efficient built environments.
Conclusion: Embracing the World of Linear Expansivity
As we conclude our exploration of linear expansivity, I hope you’ve gained a newfound appreciation for this fundamental property of matter. From the way objects transform with temperature changes to the critical role of expansivity in engineering and design, the impact of linear expansivity is undeniable.
Next time you feel a metal spoon warming up in your hot cocoa or notice how a wooden door fits snugly in its frame year-round, remember that it’s all thanks to the fascinating world of linear expansivity. By understanding and harnessing this natural phenomenon, we can create a more resilient, efficient, and sustainable world around us.
So, the next time you encounter a material that seems to magically expand or contract with the weather, take a moment to appreciate the intricate dance of particles that underlies this wondrous process. Linear expansivity is not just a scientific concept – it’s a force that shapes the very fabric of our physical world.
Thank you for joining me on this journey through the realm of linear expansivity. Until next time, keep exploring, questioning, and marveling at the wonders of the natural world!
THERMAL EXPANSION & THERMAL EXPANSIVITY (LINEAR, AREA and VOLUME EXPANSIVITY) JAMB AND WAEC PHYSICS
Frequently Asked Questions
What is linear expansivity and how does it affect materials?
Linear expansivity is a measure of how much a material expands in length when subjected to a temperature change. When a material is heated, its molecules gain kinetic energy, causing them to vibrate more and occupy a larger space, leading to an increase in length. The linear expansivity coefficient quantifies this change in length per unit change in temperature for a material.
How is the linear expansivity coefficient calculated?
The linear expansivity coefficient (α) is calculated using the formula: α = ΔL / (L * ΔT), where ΔL is the change in length, L is the original length, and ΔT is the change in temperature. The unit of linear expansivity coefficient is per degree Celsius (°C) or per Kelvin (K).
What are the factors that influence the linear expansivity of a material?
Several factors influence the linear expansivity of a material, including its chemical composition, atomic structure, and bonding forces. Generally, materials with stronger intermolecular or interatomic bonds tend to have lower linear expansivity coefficients, meaning they expand less for a given temperature change compared to materials with weaker bonds.
How does linear expansivity play a role in engineering and construction?
In engineering and construction, understanding the linear expansivity of materials is crucial for designing structures that can withstand temperature fluctuations without experiencing significant deformation or stress. By considering the linear expansivity coefficients of materials, engineers can make informed decisions about material selection, joint design, and overall structural integrity.
Can linear expansivity cause issues in everyday objects?
Yes, linear expansivity can cause issues in everyday objects, especially when different materials with varying linear expansivity coefficients are combined. For example, if a metal pipe is tightly fitted inside a plastic connector and exposed to temperature changes, the mismatch in linear expansivity can lead to cracks or leaks due to the differential expansion and contraction of the materials. It is important to account for linear expansivity effects in the design and maintenance of objects to prevent such issues.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding linear expansivity is crucial for various applications. The concept of linear expansivity relates to how materials expand or contract with temperature changes. It plays a significant role in engineering, construction, and everyday objects. By considering linear expansivity, engineers can design structures that can withstand temperature variations effectively. Mastering this concept is essential for ensuring the durability and functionality of materials and structures.




